|
Question: What is mean kinetic temperature (MKT) and how is it calculated? Are there software programs that can be used to calculate it?
Answer:
What it is:
Mean kinetic temperature is defined as "the single calculated temperature at which the total amount of degradation over a particular period is equal to the sum of the individual degradations that would occur at various temperatures. It may be considered as an isothermal storage temperature that simulates the non-isothermal effects of storage temperature variations."
What it is not:
It is not a simple arithmetic mean; it differs in that higher temperatures are given greater weight in computing the average. Disproportionate weighting of higher temperature in a temperature series, according to MKT, gives proper recognition to the accelerated rate of thermal degradation of products at higher temperatures. It is not a perfect process, but it is the standard.
How is it calculated?:
The following can be used if the temperature readings are taken at the same time interval (i.e., every 24 hours).
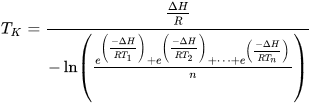
Where
- TK is the mean kinetic temperature in degrees kelvin
- ∆ H is the activation energy (in kJ)
- R is the gas constant (in J mol-1 K-1)
- T1 to Tn are the temperatures at each of the sample points in degrees kelvin
- n is the number of sample time points.
Does it have to be done manually?
No, in fact, there are three basic ways to obtain the MKT from your temperature data, as follows:
- Manually for those of you that enjoy working with a calculator. (Difficult)
- Using an Excel Spreadsheet Calculator. (Medium)
- Using a commercial software package or device. (Easy)
Using the manual method, here are the steps to follow (from the Vacker resource below):
- Convert �C to kelvin by adding 273.15 to each reading.
- Calculate ∆H/(R � Temperature Reading). Delta H = 83.14472 kJ/mole & Gas Constant = 0.008314472 kJ/mole/degree.
- Calculate the sum of all results of Step 2.
- Divide the result of Step 3 by the number of readings.
- Calculate natural logarithm of the result in Step 4.
- Calculate the numerator Delta H divided by Gas Constant.
- Calculate result of Step 5 by result of Step 6.
- Convert kelvin to degree centigrade. This gives the MKT value.
Templates using the Excel spreadsheet can be downloaded from the Internet at no cost.
Also, the USP has a new proposed chapter titled "Using Mean Kinetic Temperature to Evaluate Temperature Excursions During Storage and Transportation" that is proposed to be in Pharmacopeial Forum 45(3): [May-Jun 2019].
Resources:
Dickson
https://www.dicksondata.com/blog/measure-mean-kinetic-temperature-excel-calculator-mkt-formula-download-free/
Vacker
https://www.temperaturemonitoringuae.com/how-to-calculate-mean-kinetic-temperature-mkt-in-excel/
Loyd V. Allen, Jr., PhD, RPh
Editor-in-Chief
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding
Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy Twenty-second edition
|